Machinery
Machinery Directive's harmonized standards: The Complete Guide
Introduction
Harmonized standards for the Machinery Directive play an important role in the design and verification process of machinery, emphasizing product safety and quality. Their knowledge becomes fundamental.
In this article, we will delve deeply into the concept of technical standards, explain the different types of standards identified as A, B1, B2, and C, explore the meaning and significance of harmonized standards for the Machinery Directive, and thoroughly analyze the crucial role that technical standards play in both the certification process and the design phase to reflect the state of the art. Finally, we will see the process of declaring the application of harmonized standards.
What is a Technical Standard?
Let’s begin by defining: what is a technical standard? Technical standards are documents developed by technical committees: groups of experts collaborating to establish technical specifications and requirements for products, services, or processes. These committees comprise competent professionals who rely on detailed research, practical experience, and risk assessments to create guidelines aimed at improving quality, efficiency, and safety within specific sectors.
Technical committees consist of individuals who discuss very important sector-specific issues and specific points that must be thoroughly addressed to facilitate design and enhance the safety standard of products circulating in the international or European market.
Technical standards are not legislative acts; unlike directives and regulations, they are not mandatory for machinery manufacturers.
Different Types of Standards A, B1, B2, and C
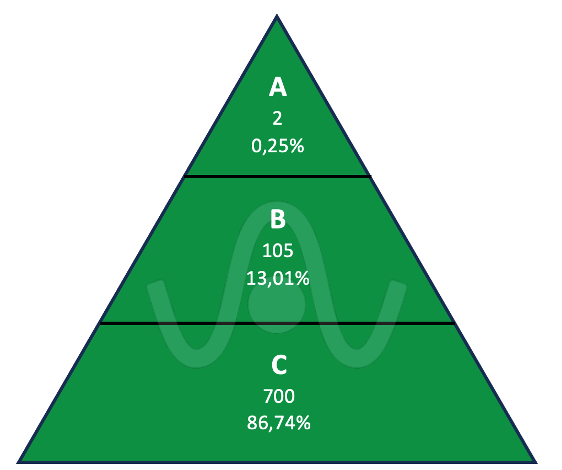
Technical standards are classified into different types A, B, and C:
- Type A standards provide general guidance that can be broadly applied to all types of machinery.
- Type B standards address aspects related to design and specific risks, and they are divided into Type B1 standards if they refer to general aspects of machinery safety, and Type B2 standards that concern specific technical aspects of safety devices.
- Type C standards representing the largest category, cover specific categories of machinery, such as the EN ISO 4254 “agricultural machinery” series and the EN 415 “packaging machinery” series.
In the diagram below, we see the structure of the current version of the list of harmonized standards, totaling 807 standards distributed as seen in the data within the pyramid.
Harmonized Standards for the Machinery Directive: Definition and Benefits
If standards are “harmonized” with the Machinery Directive, they play an even more essential role for the manufacturer: these standards are identified by the European Union (EU) as official technical references, intended to demonstrate product compliance with the essential safety requirements established by the Machinery Directive. In practice, they serve as a solid foundation upon which to build product compliance, providing detailed guidelines and technical specifications for the design, manufacture, and safe use of machinery.
Harmonized standards for the Machinery Directive are voluntary, like all standards. However, if applied correctly, they provide the manufacturer with a “presumption of conformity” with the requirements of the Machinery Directive, ensuring that these requirements for minimum safety are met.
For machinery subject to control, certification bodies rely on harmonized standards for the Machinery Directive to conduct detailed assessments and tests to verify product compliance; if all requirements are met, they issue the necessary certificate of conformity. As a result, harmonized standards provide a reliable framework to demonstrate that a product has been accurately evaluated and meets high safety standards.
Furthermore, harmonized standards for the Machinery Directive facilitate access to markets in other countries because they use recognized compliance standards throughout the European and often international territory.
How to Recognize if a Standard is Harmonized to the Machinery Directive
Understanding whether a technical standard is harmonized is important if you want to take advantage of the presumption of conformity and be certain that your product respects the state of the art.
Harmonized standards for the Machinery Directive are published in the Official Journal of the European Union and contain references to the corresponding directive or regulation.
The list of harmonized standards is periodically updated by the European Union as references are updated and new standards are added for new product categories.
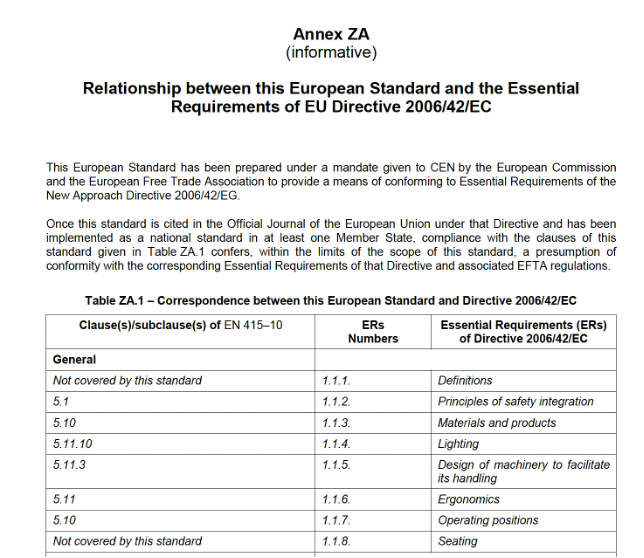
A technical standard can also be harmonized with respect to multiple legislative acts. Details of harmonization can be found in the “Z” annexes contained within the normative texts. These annexes explain which directives the standard is harmonized with and which requirements are covered by the presumption of conformity (see example of Annex ZA below).
Attention! Applying a harmonized standard for the Machinery Directive does not exempt the obligation to conduct a risk analysis. Harmonized standards rarely cover all requirements, our product must always be subjected to a dedicated analysis.
How to Declare the Application of Harmonized Standards for the Machinery Directive
Correctly declaring the application of harmonized standards for the Machinery Directive is essential to demonstrate product compliance. The standards for which you wish to enjoy the presumption of conformity must be explicitly stated in the CE conformity declaration or in the product incorporation declaration, attesting that the product has been developed, tested, and evaluated in line with the requirements of the harmonized standard.
The declaration of conformity provides clear evidence of compliance during the assessment and certification process, facilitating approval by competent authorities.
Conclusion: The World of Harmonized Standards for the Machinery Directive
In this brief journey into the world of harmonized standards for the Machinery Directive, we have explored the very foundations upon which machinery safety and quality stand. Technical standards, developed by expert committees, are the universal language that brings together manufacturers, designers, and assessment authorities, guiding them toward the state of the art in terms of safety, efficiency, and reliability.
We have discovered how harmonized standards for the Machinery Directive play a central role in the certification process, providing a clear and objective reference for evaluating and demonstrating product compliance.

WAVES Engineering S.r.l.